Key Takeaways
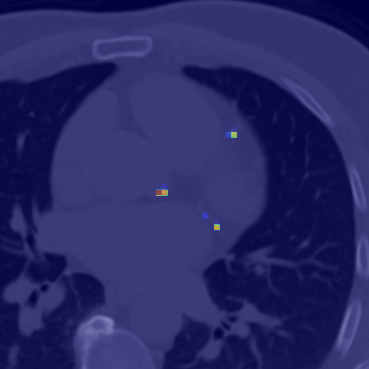
- AI Model Breakthrough: The DINO-LG model significantly improves coronary artery calcification (CAC) detection on CT scans, achieving 89% sensitivity and 90% specificity.
- Reduced Diagnostic Errors: False negatives and false positives drop by 49% and 59%, respectively, enhancing confidence in clinical assessments.
- Efficient and Cost-Effective: Targeting relevant CT slices for analysis streamlines diagnostic workflows, reducing unnecessary imaging and healthcare costs.
Quick Summary
Coronary artery disease (CAD) remains a leading cause of mortality, requiring effective screening tools like coronary artery calcium (CAC) scoring via CT scans. Researchers have addressed limitations of traditional models by introducing DINO-LG, an AI model using self-supervised learning with label guidance. Without requiring annotated datasets, the model detects calcifications with greater precision, reducing false negatives and false positives. This improvement allows clinicians to confidently rule out calcifications in low-risk patients while minimizing redundant imaging. Combining DINO-LG with a UNET-based segmentation model for targeted slices enhances scoring accuracy, reducing overall healthcare costs and improving CAD risk assessment protocols.
Disclaimer: I am not the author of this great research! Please refer to the original publication here: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2411.07976.pdf