Key Takeaways
- Enhanced Full-Body Tracking: Researchers have developed XR-MBT, a system that utilizes depth sensing and self-supervised learning to achieve real-time full-body motion tracking in extended reality (XR) environments.
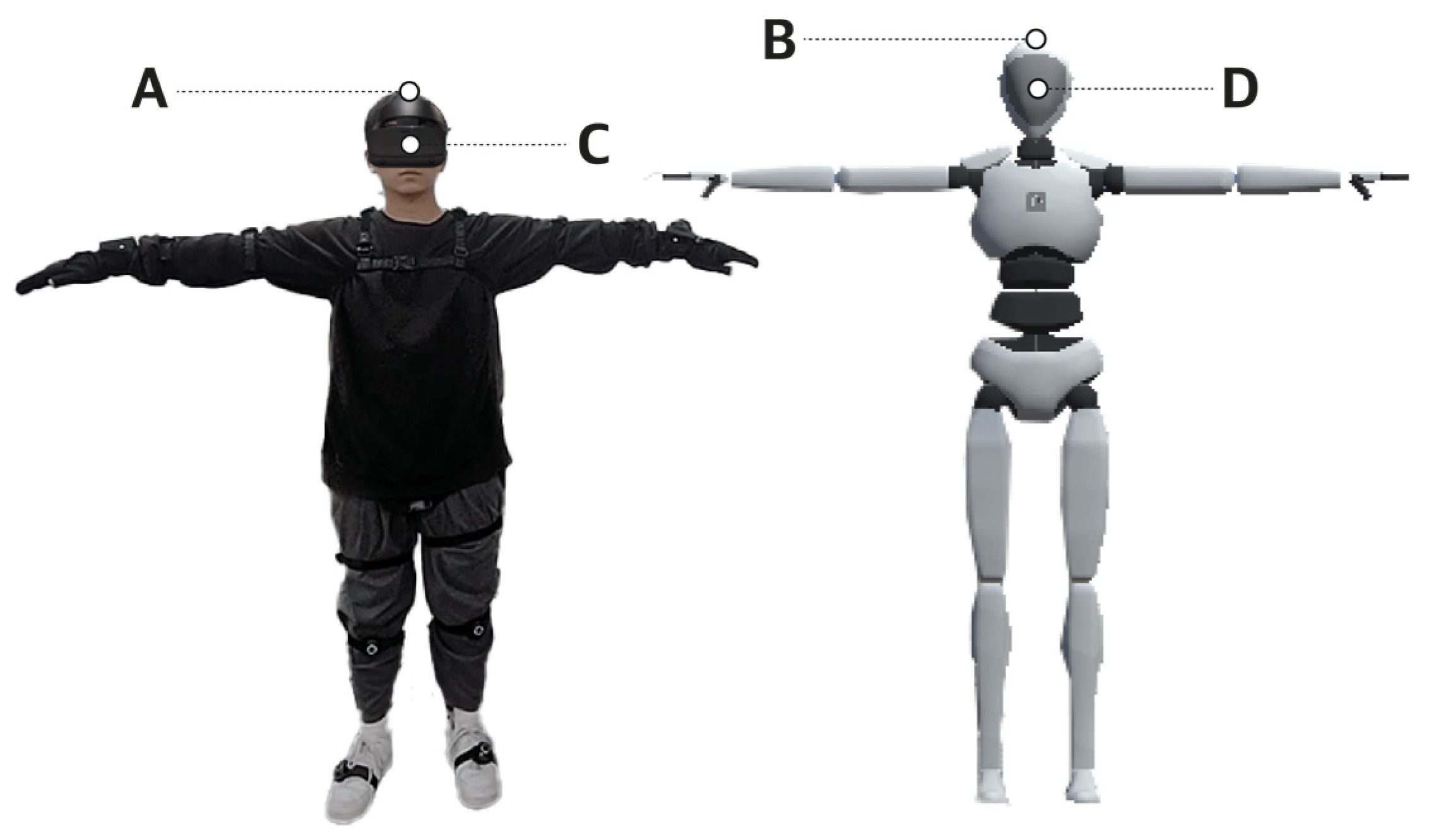
- Overcoming Sensor Limitations: By integrating depth data with existing head and hand tracking, XR-MBT effectively tracks lower-body movements without the need for additional sensors.
- Improved User Representation: This advancement enhances the authenticity of virtual avatars, fostering more immersive social interactions in augmented and virtual reality settings.
Quick Summary
Achieving realistic full-body motion tracking in extended reality (XR) environments has been challenging due to the absence of dedicated sensors for lower-body movements. Traditional methods rely on tracking the head and hands, often resulting in incomplete or synthesized body motions. Addressing this, researchers have introduced XR-MBT, a system that leverages depth sensing—a technique that measures the distance of objects from a sensor—to capture comprehensive body movements. By combining depth data with self-supervised learning, XR-MBT accurately maps body parts and refines pose estimations in real-time. This integration enables the system to track leg movements effectively, enhancing the realism of virtual avatars without requiring additional hardware. The development of XR-MBT represents a significant step forward in creating more immersive and socially engaging experiences in augmented and virtual reality.
Disclaimer: I am not the author of this great research! Please refer to the original publication here: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2411.18377.pdf